Dermatoscopy (surface microscopy or epiluminescence microscopy) is a non-invasive diagnostic technique used for the early diagnosis of melanoma and for the evaluation of pigmentary and non-pigmentary lesions of the skin and visible mucous membranes, synonyms are dermoscopy, surface microscopy and epiluminescence microscopy.
 |
 |
 |
It allows to evaluate the disposition of the pigment inside the epidermis and dermis. This examination is performed with an instrument equipped with a loupe with magnification that can vary, but normally a 10 x or 20 x magnification is used. There are manual instruments which allow a detailed view, but have the drawback of not archiving the images and digital instruments (video dermatoscopy), which allow the archiving and comparison of images over time, and also allow the study of the lesion with filters). It is also possible to adapt a special lens (Dermaphot, Heine) to a digital or conventional camera to obtain a photograph of the dermatoscopic image.
Of rarer use is the stereomicroscopic which allows a three-dimensional vision of the cutaneous architecture, but the large dimensions limit its use. There are also instruments which use the contact of the lens through an immersion oil and polarized light instruments (the first instrument , DermLite, was introduced in 2001 in California by 3rd Gen).
Dermatoscopy has completely changed the dermatologist’s approach in the diagnosis of melanoma by increasing both specificity and sensitivity. A dermatologist expert in this method can use this tool to perform a detailed study of all nevi, can also perform an accurate differential diagnosis between melanoma and other skin lesions (pigmented basalioma, pigmented seborrheic keratosis, hemangiomas, etc.) and can also easily identify nevi risk so they can be removed before they develop into melanoma. Among the limitations of the method there are first of all the interpretation of the images which obviously depends on the experience of the dermatologist (from studies it seems that used by non-expert doctors can reduce the clinical ability to identify a melanoma) and also the false negatives and positives Finally, some areas such as the interdigital one are difficult to analyse; in the case of nevi or nail melanomas there are no specific pictures and everything depends on the operator’s experience. This test is also reliable in dark race patients (British Journal of Dermatology, October 2006)
The examination is painless and is performed by placing the instrument on the skin (as occurs in ultrasound) after having sprinkled the lesion with oil or ethanol (in the case of the instrument with polarized light, the instrument is only placed on the skin). Dermatoscopy uses specific semiotics and its basis is the concordance between dermatoscopic parameters and cutaneous histological structures. Some parameters are important for the diagnosis of melanoma
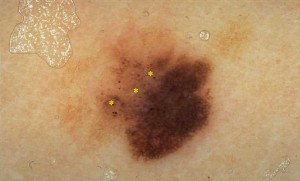
Pigmentary reticulum: it is the most important parameter, the lines of the rete correspond to the elongated epidermal ridges and the spaces of the rete to the dermal papillae; appears regular and shaded in the periphery in benign lesions, appears irregular with coarse meshes, with pigmentation of variable intensity, not shaded in the periphery and asymmetrical in suspicious lesions
Pigmentary pseudoreticulum: it is an interruption of pigmentation by hypopigmented patches determined by hair follicles and glandular outlets. In lentigo maligna due to the atypical melanocytes increased in number, it appears irregular and coarse
Radial striae and pseudopodia: often visible in superficial spreading melanoma, they are a sign of radial growth of the tumor, sometimes when they are arranged around the entire edge of the lesion it could be a Reed or Spitz nevus
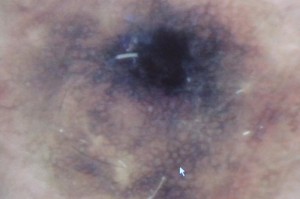
White/bluish veil: often present in melanoma, rarely in Spitz/Reed nevi. It is due to orthokeratosis with hypergranulosis associated with confluent nests of pigmented melanocytes in the dermis.
Bluish gray areas: May be associated with regressing melanoma and due to the presence of hemosiderin or melanins in melanocytes or melanophages. They may appear as peppered and speckled areas or be well defined with jagged edges
Black points (accumulations of melanin or melanocytes in the stratum corneum) and brown blood cells: They correspond to accumulations in the papillary dermis or at the junction of pigmented melanocytes or melanophages; they are roundish spherical bodies of variable color. If arranged in the periphery (mainly in adults) and irregular in shape and size, they can be an indication of a suspected lesion. Red-white blood cells are present in melanoma and are due to increased vascularity
Diffuse pigmentation: Patchy localized areas of pigmentation may be significant for melanoma
Depigmentation: may be a sign of a regressive phase of melanoma and correspond to areas of fibroplasia, telangiectasias and loss of melanin
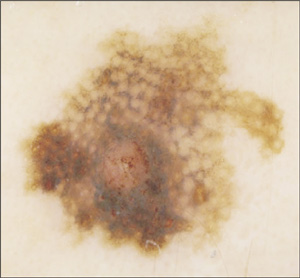
Miliary cysts and comedonic-like outlets: they are roundish whitish or yellowish areas are often present in seborrheic keratoses, sometimes they are also present in melanoma and melanocytic nevi. They represent keratin-filled cysts (myal cysts) or keratin-filled hair follicles (comedo-like outlets)
Blackish-red lakes: present in angiomas
Maple Leaf Areas: Predominantly found in basal cell epitheliomas. They correspond to highly pigmented basaloid cells within nests of malignant cells
Vascular structures: tree-like features are present in basal cell epithelioma, comma-like features in dermal nevi, pin-like features in superficial epithelial tumors, clip-like appearance and combined forms may be a sign of melanoma
Each of these parameters is not specific for melanoma and the diagnosis must be based on a pattern analysis that takes into account the various parameters detected.
Then there are some algorithms that are used for the diagnosis of melanoma which allow, through the score obtained, to evaluate the possible malignancy of a lesion; the best known algorithms include: Seven point check list, dermoscopic ABCD, Seven features for melanoma,
Menzies scoring method, CASH
I recommend reading an article available on the web: Dermatoscopy of Pigmented Skin Lesion: HP Soyer, G Argenziano, S. Chimenti, V. Ruocco